
Test planning suffers due to poor requirements
Test planning is a critical part of an in-depth test strategy and includes the definition of the test objectives, scope, and the means and the schedule for achieving them, among other things.
Determining the extent of test coverage and prioritizing test cases are essential elements of a robust testing strategy, serving a crucial role in assuring the comprehensive validation of the software under test.
Unfortunately, testing teams face challenges due to ambiguous, changing, or incomplete requirements, making it difficult to establish a robust foundation for the test planning process.
This creates a cascading impact on the prioritization of testing efforts, resulting in resources being allocated to less critical test scenarios, potentially overlooking important issues, and ultimately leading to inadequate test coverage.
Approaches to address gaps in test coverage
As we discussed before, coverage gaps commonly occur when requirements are misunderstood, specifications are poorly defined or ambiguous and changes in the software are not appropriately incorporated into the test planning.
To tackle these challenges, test teams should embrace formal test design methods to guarantee comprehensive coverage of all aspects outlined in the requirements. Implementing a traceability matrix, linking requirements to test cases, further ensures comprehensive coverage.
Additionally, encouraging collaboration among development, testing, and business teams early in the process to clarify requirements helps mitigate the risks associated with poor requirements.
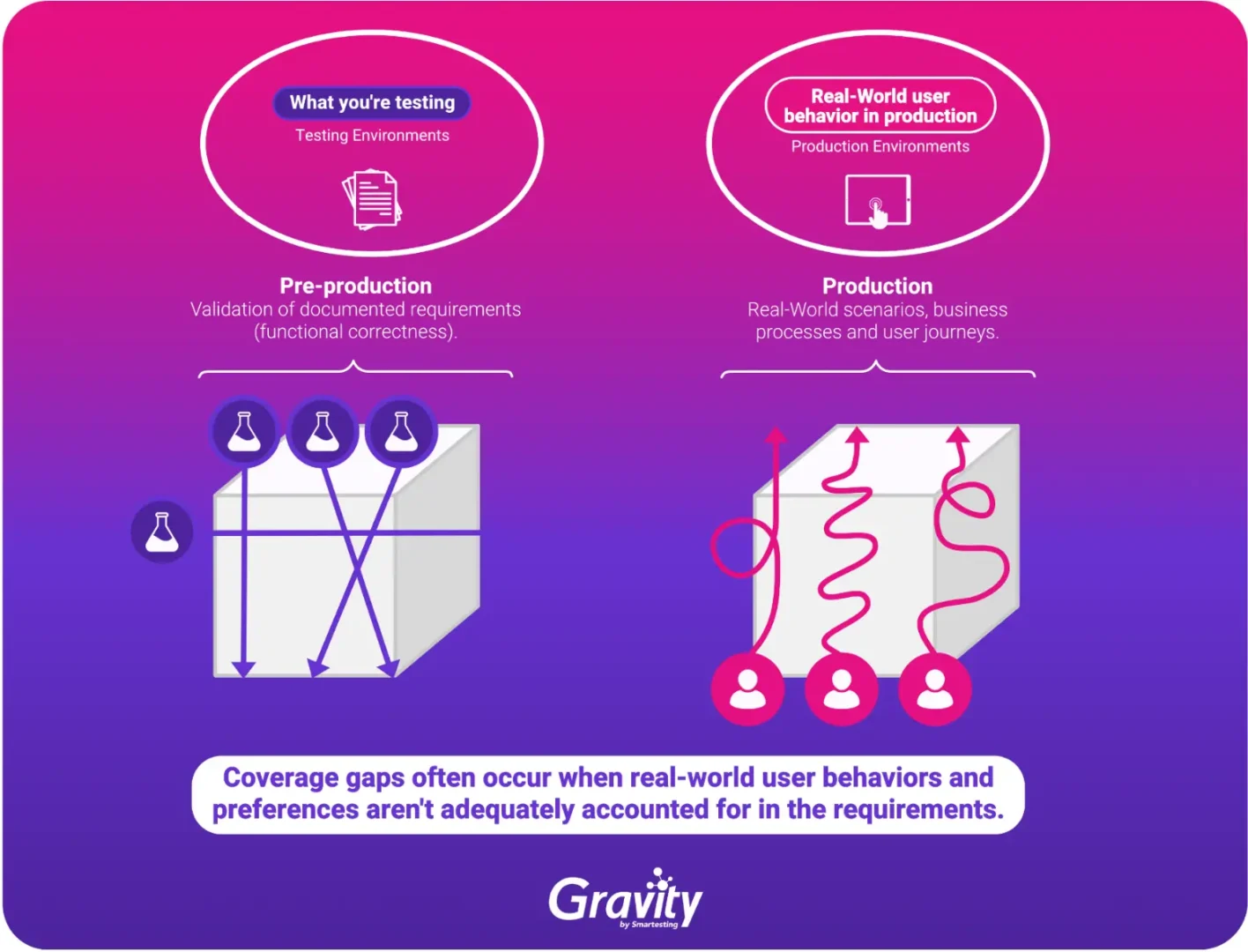
Yet, coverage gaps can arise when the requirements fail to adequately capture real-world user behaviors and preferences. Anticipating and comprehensively accounting for all user interactions and behaviors in written requirements proves to be a challenging task for product owners and business analysts.
Finding the needle in multiple disconnected tools
To boost test coverage and align the test prioritization with real-world usage, testing teams can analyze logs from both production and test environments, uncovering valuable insights and quality analytics.
Testing teams need to implement tools and processes to actively monitor, measure, and analyze user behavior when interacting with the live application. Additionally, it’s essential to observe how tests interact with the application during test runs to reveal disparities between how the application is used by real-world users and how it is tested.
In the market, tools like Google Analytics, Amplitude, SmartLook, Datadog, and others assist in collecting and analyzing telemetry from any environment. Designed with different purposes in mind, these tools serve various teams, such as Product and Marketing Analytics, Observability, and Application Performance Management. Despite their versatility, they may not be the optimal fit for testing purposes.
Considering this, a major challenge is that these tools aren’t designed to meet the specific needs of testing teams. This limits their ability to get the most out of the tools and stops them from seeing both how the software is used in the real world and during test runs and extract meaning from it.
Enhancing Test Planning with Quality Intelligence
Gravity is a unified platform designed to help testing teams monitor and leverage insights from both production and testing environments, enhancing the efficiency of the test strategy. It consolidates key data and insights into a single solution for easy access and analysis.
Its primary function is to produce “Quality Intelligence” by processing the ingested data through machine learning algorithms. This involves translating raw data into meaningful insights using techniques such as pattern recognition, trend and correlation analysis, anomaly and outlier detection, and more.
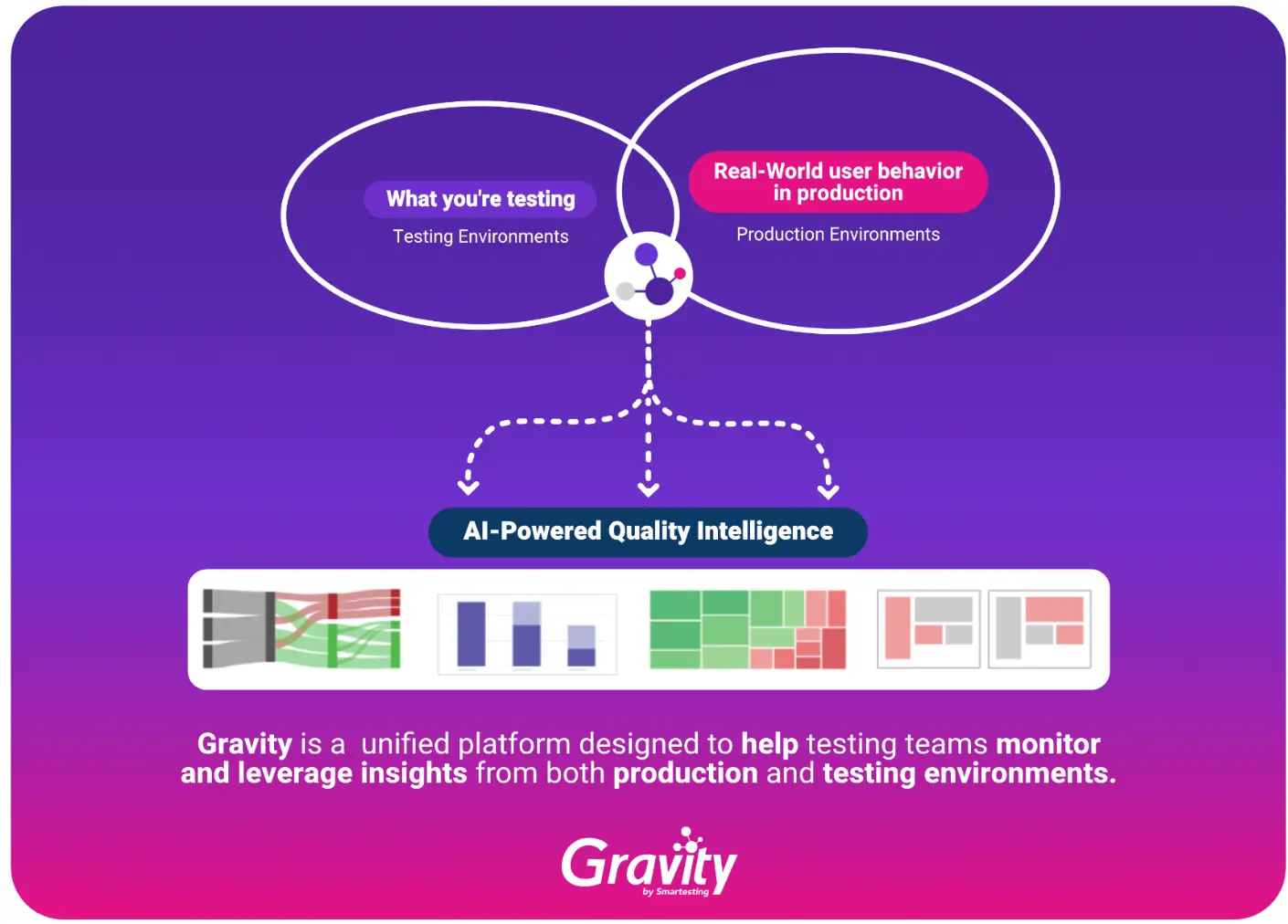
Gravity’s ability to monitor production and testing environments allows it to conduct a comprehensive test gap analysis. By comparing the paths taken by real user interactions in live production with the tests executed in testing environments, Gravity generates insights to enable testing teams to spot gaps in coverage, identify features that are either over-tested or under-tested, and recognize redundant testing efforts in less critical areas.
Gravity utilizes pattern recognition and AI (Artificial Intelligence) to automatically generate test cases for areas lacking test coverage, whether they are manual tests or automated scripts for test automation tools like Cypress, Playwright, and others. This feature not only reduces the burden of test case creation but also leads to a decrease in maintenance overhead.
Since it relies on real usage data collected from production environments, this enables data-driven test case prioritization, focusing test coverage on high-impact areas that directly affect the end user experience. By bridging assumptions from requirements with real-world usage insights, Gravity helps in optimizing test planning for improved efficiency and agility.
Conclusion
Understanding user behaviors in production not only elevates test coverage and prioritization by focusing on genuine user experiences but also acts as a powerful antidote to the limitations of the traditional requirement-based testing approaches.
It ensures that testing efforts are not confined to the rigid boundaries of documented requirements but rather extend to the dynamic and evolving landscape of user interactions, contributing to a more comprehensive and user-centric testing paradigm.
Gravity represents a remarkable advancement in the field of Quality Engineering, empowered by cutting-edge AI (Artificial Intelligence), with the aim of enabling testing teams to deliver higher-quality software products.
Author

Cristiano Caetano, Head Of Growth at Smartesting
Software testing authority with two decades of expertise in the field. Brazilian native who has called London home for the past six years. I am the proud founder of Zephyr Scale, the leading Test Management application in the Atlassian ecosystem. Over the last ten years, my role has been pivotal in guiding testing companies to build and launch innovative testing tools into the market. Currently, I hold the position of Head of Growth at Smartesting, a testing company committed to the development of AI-Powered testing tools.
Smartesting is an exhibitor at EuroSTAR 2024, join us in Stockholm.





