Often automated testing is seen as an act by the team that is creating the software. It is a task to ensure quality of the software before it is shipped. However there is an important usage of test automation that can take place AFTER the software is shipped. And it is done BY the CUSTOMER!
The Need:
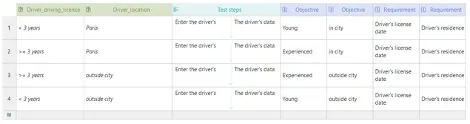
Customer organizations which buy software don’t just use one particular software. For different aspects of their business, they use different software applications. These applications are integrated together in various workflows, so that they work in tandem to improve employee productivity. Teams in such organizations use these applications on a daily basis and their productivity would falter if any of the software applications fail to function as expected. It is a reality of the current times that each of these applications may be updated 2 to 3 times if not more times a year. And each software application may have its own release cycle/cadence. Any software update may disrupt the employee workflow and cause significant damage in terms of time and money for the company. Hence, organizations need to ensure that their workflows continue to work after any update to these software applications. Such task may be carried out by a business team or a QA team at the customer org.
Can this verification be automated? What are the challenges?
We regularly work with customers in the Automotive industry. These are the challenges faced by them.
Challenges Faced:
1) Software applications in business workflows may be built on different technology stacks. A desktop application may be used for designing automotive parts while a web based PLM application may be used for managing those designs. The interplay between these two applications would be important for the customer teams. Most automation tools do not support automation of multiple technologies.
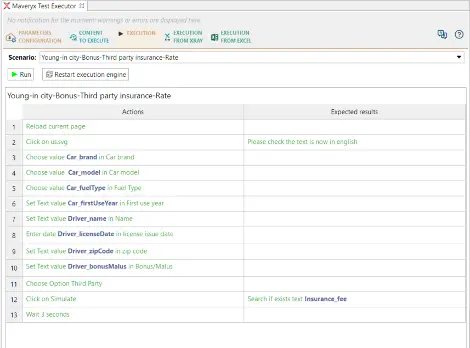
2) Applications once shipped behave mostly as a black box. They need to be exercised mostly via the Graphical User Interface (GUI). Importantly, we need to mimic the end user’s usage pattern, so GUI becomes significant.
3) Teams that verify such functional continuity will be small and more focused on the business aspects than the automation aspects. They may not have technical know-how (or time) to automate such third party applications using traditional programmatic tools.
So teams look for an automation tool that:
1) Can work across technologies like desktop, web, java, SAP etc.
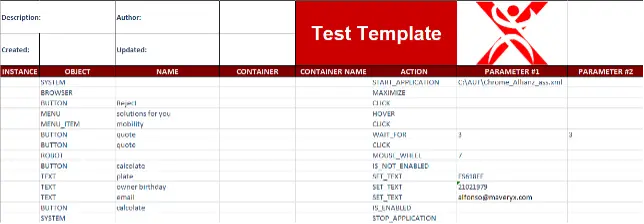
2) Is easy to use – preferably low or no code
3) Has good support. Since the team may not be very technical, a good support team ensures any edge cases can be handled correctly and quickly
Over the past few years, Sahi Pro has helped a lot of customers achieve such business process automation, especially in the Automotive industry. With the upcoming Sahi Pro v11, automation becomes even more easy because of the no code flowcharts interface. The Flowcharts interface makes visualizing and managing automation very accessible to non-technical testers and business users. Sahi Pro 11 Beta is currently available. Reach out to us to play with Sahi Pro 11 Beta to get a POC done on your automation needs.
Author

Narayan Raman, CEO
Narayan is the CEO and founder of Tyto Software. He is the author of open source Sahi and the architect of Sahi Pro.
Sahi Pro is an exhibitor at EuroSTAR 2024, join us in Stockholm.