Testing software is the process of measuring a program against its design to find out if it behaves as intended. It’s performed in order to ensure that the developed app or system meets requirements and to enable further development of the product.
In the realm of software development, automated testing has become indispensable. Whilst it may require an initial investment, over time, it can more than repay the upfront cost. Manual testing offers advantages and disadvantages, such as being more prone to error yet providing insight into your visuals. Ultimately, it all comes down to what your project requires and the resources you have.
What is manual testing?
Manual testing is a type of application testing where QA or software engineers are tasked to execute test cases manually without using any automation tools. In this process, the testers utilize their own experience, knowledge, and technical skills to perform testing on the application or software in development. It’s done to find bugs and any issues in the software or application and ensure that it works properly once it goes live.
In contrast to automated testing, which can be left to run on its own, manual testing necessitates close involvement from QA engineers in all phases, from test case preparation through actual test execution.
Manual software testing with Test Center
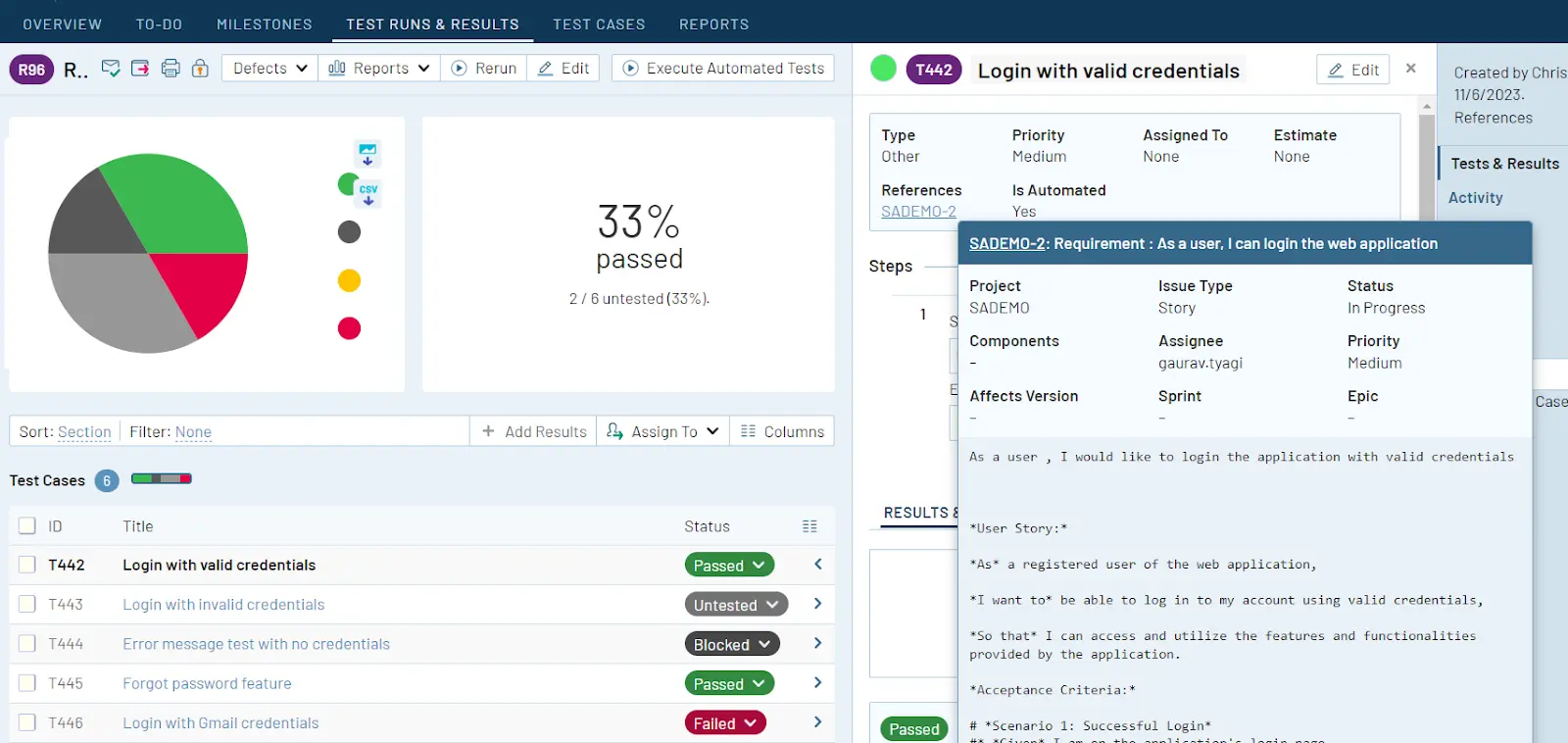
Test Center, one of the tools in the Qt Quality Assurance Tools portfolio, provides a streamlined system for managing manual testing results, providing an overview of these alongside the automated test results. Additionally, there’s a test management section where the manual testing procedures and documentation can be set up and managed.
It has a split screen design where the left is for creating and managing the test hierarchy and includes making test suites, test cases, features, and scenarios. Meanwhile, the right pane is where changes to the test case or scenario’s description and prerequisites are made. It is also utilized to design and administer each part of a test.
What is automation testing?
Automation testing is the use of software tools and scripts to automate testing efforts. A tester will have to write test scripts that instruct the computer to perform a series of actions, such as checking for bugs or performing tasks on the target platform (e.g., mobile app or website). It helps to improve test coverage by enabling the running of more test cases than manual testing allows, and in less time.
Users with experience in scripting are needed. Tools like Selenium, QTP, UFT, and Squish are used for automation. Squish supports a number of non-proprietary programming languages, including Python, JavaScript, Ruby, Perl, and Tcl, thus, knowledge of them is advantageous.
Automated software testing with Squish
With Squish, you can automate your GUI testing across cross-platform desktop, mobile, embedded, and online apps and is usable on different development platforms. It simplifies what is typically a laborious and error-prone process – testing the user interface of today’s new and evolving apps.
Squish supports functional regression testing and automated GUI functional testing. It also helps you to automatically test your application in different environments, simulating users’ actions in a controlled and repeatable manner.
It includes:
- Full support for all leading GUI interfaces
- Complete compatibility for various platforms (PCs, smartphones, web, and embedded platforms)
- Test script recording
- Robust and trustworthy object identification and verification techniques
- Independent of visual appearance or screenshots
- Efficient integrated development environment (IDE)
- A large selection of widely used scripting languages for test scripting
- Full support for behavior-driven development (BDD)
- Full control with command line tools
- Support for integrating test management with CI-Systems
Choosing manual or automated testing – Pros & Cons
There are a number of factors to consider when choosing between the two. For one, the biggest challenge facing software developers is the deadline. If the completion date is missed, then the company could lose customers. There is also an issue with budgets, as automated testing will require setup and maintenance.
Both solutions offer advantages and disadvantages, so you will need to examine them based on your needs. Here’s a closer look:
Manual testing
Pros:
- Costs less than automated testing to initiate
- Gives room for human perception, which helps provide insights into user experiences
- Can provide valuable human feedback on your visuals (such as the colors, fonts, sizes, contrast, and button sizes used)
- More efficient when test cases only need to be run once or twice
- Small modifications can be applied quickly without having to be coded
- Best for exploratory, usability, and ad-hoc testing
Cons:
- Can be time-consuming and labor-intensive for QA engineers or testers
- There is a possibility of human error
- Cannot be reused – repetitiveness can lead to the work being quite tiring and dull for QA engineers or testers
- Scales poorly as more manual testers would be needed for larger and more sophisticated applications
Automated testing
Pros:
- Works faster since it doesn’t rest or sleep
- Has the ability to find more defects
- Good for repetitive test cases
- Can run multiple tests simultaneously
- Increases the breadth of coverage compared to manual
- Can be recorded and reused for similar test cases
- Best for regression, performance, load, and highly repetitive functional test cases
- Larger projects may require more manpower, but still less than manual testing as only new test scripts need to be written
Cons:
- Exploratory testing is not possible
- Needs to be coded
- Unable to take human factors into account so it is unable to provide user experience feedback
- Small modifications will have to be coded which can take time
- Initial test setup and the required maintenance can be expensive
In most instances, automated testing provides advantages, but all technology has limits. When creating anything to enhance the consumer experience, human judgement and intuition provided by manual testing can make a difference.
Deciding on whether automated or manual testing is better for your organisation will largely depend on the number of test cases you need to run, the frequency of repeated tests, and the budget of your team.
Ideally, your organisation should incorporate both as they each have their own merits. There are many instances where manual testing is still necessary and where automated testing could be more efficient. Either way, these two software testing methods are both important assets.
Read more about quality assurance from our comprehensive guide here: The complete guide to quality assurance in software development
Author

Sebastian Polzin, Product Marketing Manager,
Qt Quality Assurance
The Qt Company is an EXPO Gold Sponsor at EuroSTAR 2024, join us in Stockholm.