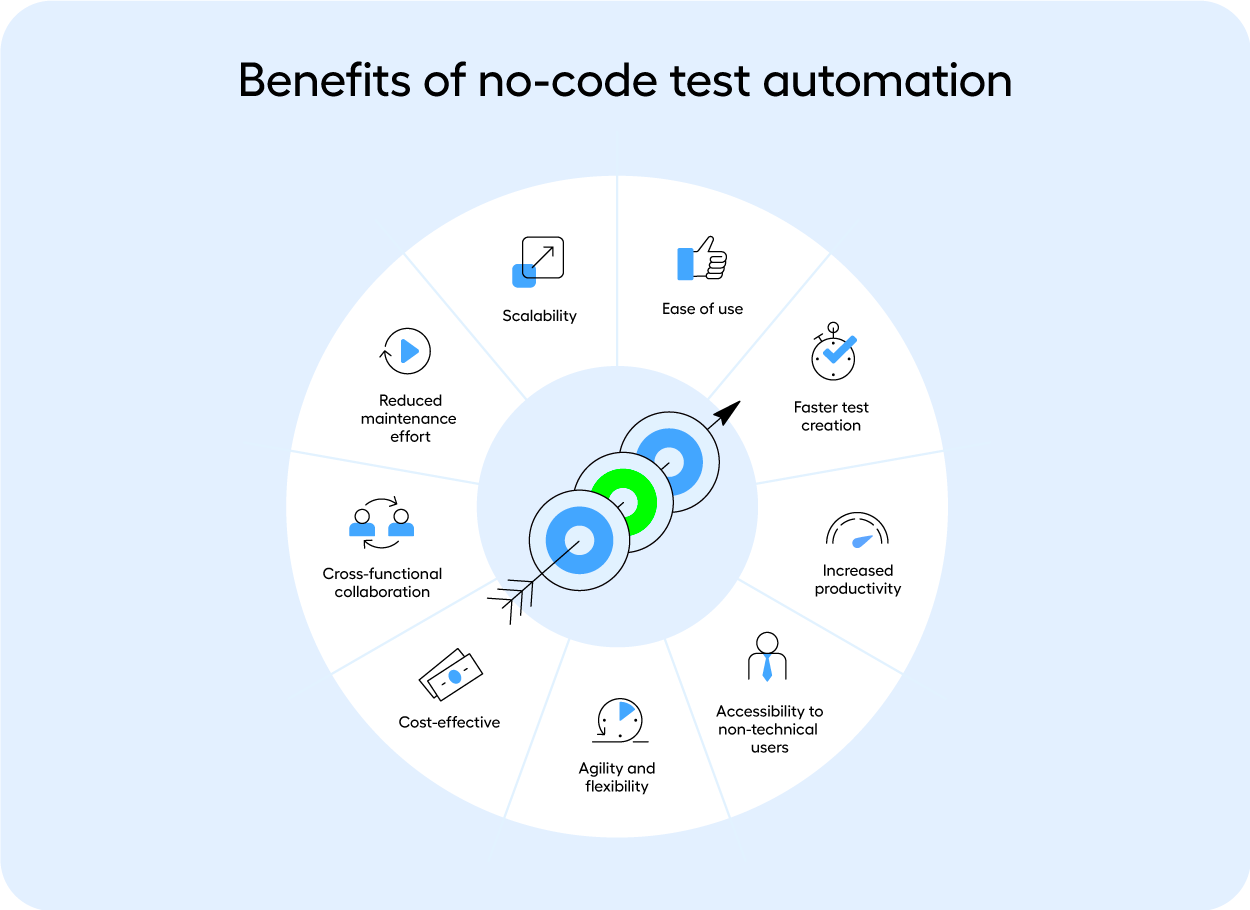
The digital landscape is evolving every day and ensuring software quality is extremely important To ensure the applications meet the standards of functionality, reliability, and performance, businesses rely on extensive testing practices. Nevertheless, there are many hurdles to overcome to conduct tests successfully and efficiently due to the sheer complexity and size of current software systems.
Overseeing test execution gets harder as businesses mature and their software ecosystems get more and more complex. Traditional approaches often result in inefficiencies, delays, and increased expenses because they use diverse tools, fragmented processes, and fragmented teams.
These challenges are easily resolved with a unified test execution infrastructure, providing an integrated structure for managing and carrying out tests over the entire software development lifecycle. Enterprises can broaden test execution with ease and maximize efficiency and quality via a unified infrastructure, which integrates testing tools, standardizes processes, and fosters cooperation.
Unified Test Execution – The Need of the Hour
Businesses frequently use an assortment of testing frameworks and tools to meet distinct technological and testing requirements. However supporting this fragmented ecosystem can be challenging and can cause problems with compatibility, integration, and overhead.
As teams or projects function independently in siloed test environments, it may result in duplication, inaccurate testing procedures, and a lack of visibility across the operation. It can hinder interactions, limit teamwork, and reduce the effectiveness of the testing process as a whole.
Establishing consistency, repeatability, and scalability in test execution requires standardizing testing procedures and centralizing testing infrastructure. Enterprises can gain greater oversight and insight over their testing attempts, enhance resource utilization, and accelerate workflows by implementing a unified approach in testing.
LambdaTest: Empowering Enterprises with AI-driven Test Execution
The unified test execution environment offered by LambdaTest revolutionized the way businesses plan, organize, and execute their testing activities. LambdaTest’s range of AI-powered capabilities enables enterprises to increase test efficiency, enhance test infrastructure management, and deliver software designed to be of better quality at scale.
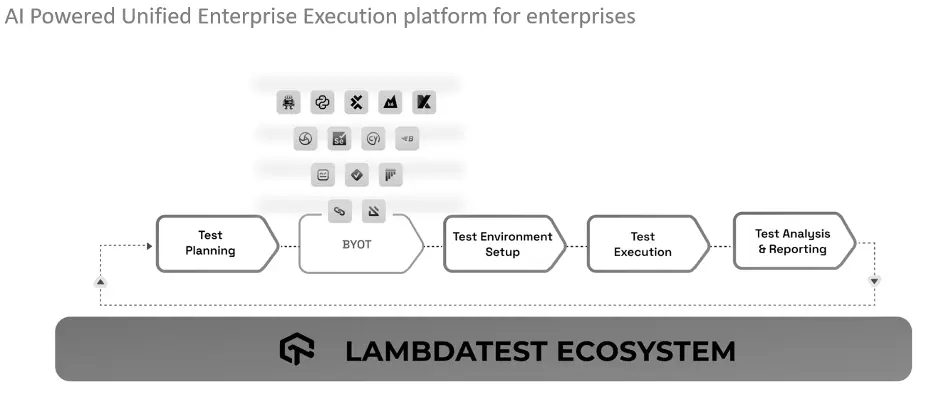
Through an assortment of innovative capabilities, LambdaTest uses artificial intelligence (AI) to improve testing processes. Its Auto Heal feature efficiently recognizes and fixes issues with the test environment in real time, minimizing interruptions and ensuring testing operations progress. The capacity to identify test failures promptly with fail-fast capabilities allows teams to address vulnerabilities early in the development cycle and accelerate resolution, thus enhancing overall efficiency. Also, test cases get intelligently prioritized by the Test Case Prioritization functionality using AI algorithms based on their impact and likelihood of failure. Teams can reduce time-to-market and improve software quality by employing this strategic approach to focus on high-risk areas, increase testing coverage within restricted schedules, and swiftly address important issues.
Moreover, GPT-powered RCA (Root Cause Analysis) offers deeper insights into the underlying causes of test failures by analyzing test results and historical data. By identifying patterns, trends, and potential correlations, the AI engine enables teams to address root causes effectively and prevent the recurrence of issues. Furthermore, the Test Intelligence module provides actionable insights derived from comprehensive test data and analytics.
By aggregating metrics, performance indicators, and user feedback, LambdaTest empowers teams to make informed, data-driven decisions, optimize testing strategies, and continuously enhance software quality.
Conclusion
LambdaTest’s unified test execution environment, enriched with AI features such as Auto heal, Fail fast, Test case prioritization, GPT-powered RCA, and Test intelligence with test insights represents a significant advancement in enterprise test automation. By harnessing the power of AI, LambdaTest empowers organizations to streamline test execution, mitigate risks, and deliver superior software products that meet the demands of today’s dynamic market landscape.
Author

Mudit Singh
A product and growth expert with 12+ years of experience building great software products. A part of LambdaTest’s founding team, Mudit Singh has been deep-diving into software testing processes working to bring all testing ecosystems to the cloud. Mudit currently is Head of Marketing and Growth for LambdaTest.
Lambdatest is an EXPO Gold Sponsor at EuroSTAR 2024, join us in Stockholm.