Accessibility testing is essential for compliance with regulations such as the European Accessibility Act (EAA). The EAA becomes a national law in all 27 EU Member States on June 28, 2025, and businesses need to be prepared. While failure to meet this deadline can result in severe penalties, achieving compliance is ultimately about much more than just avoiding fines. It’s about expanding your market share, enhancing your brand reputation, and building high quality products for everyone, including people with disabilities.
This is why testing is so essential. By putting an effective and efficient testing approach in place, you can quickly identify and fix accessibility issues early and ensure you’re building the highest quality products for all people. The question is, how do you integrate comprehensive accessibility testing while maintaining velocity and keeping costs down?
It’s a challenging question. Fortunately, there’s a clear answer.
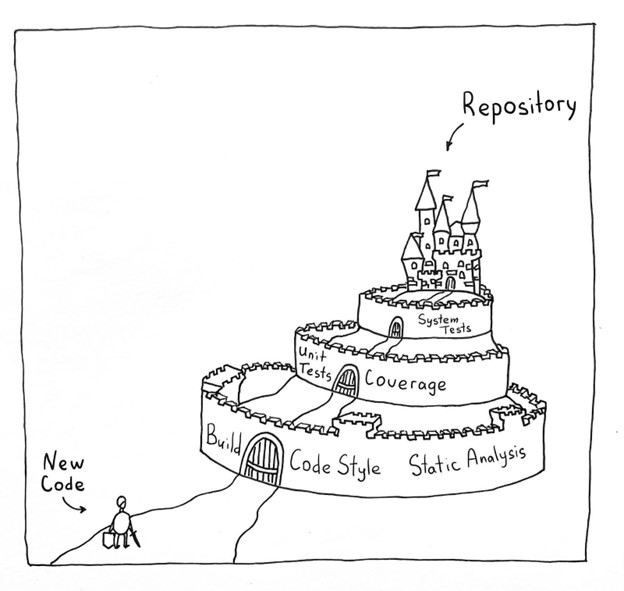
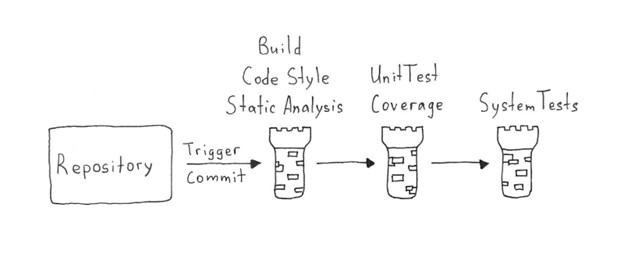
In this post, we’ll explore an approach called “shift left“, which refers to addressing accessibility issues earlier in the software development lifecycle—during development and QA—as opposed to later in production or after a product has been released, at which point the work becomes slower, costlier, and the risk of customers having a poor experience goes up exponentially. We’ll also examine how AI and automation can accelerate velocity while elevating quality.
The benefits of automated and AI-guided testing
Getting and staying compliant in a strategic and cost-effective way means prioritizing efficiency. It’s about doing the work early and accurately, avoiding re-work, and getting high-quality products out the door faster.
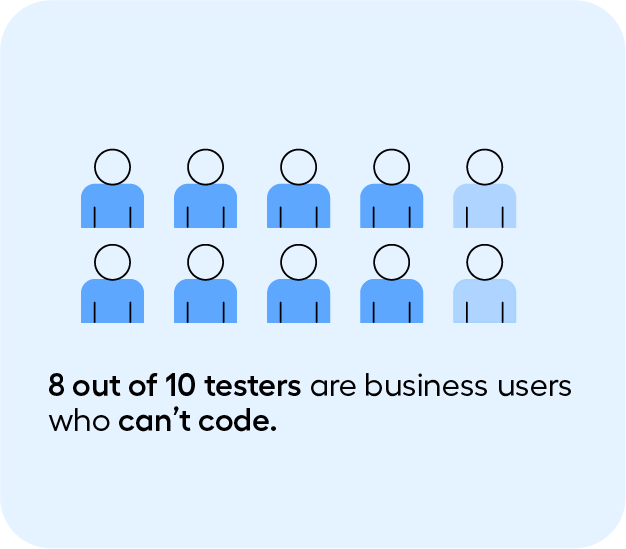
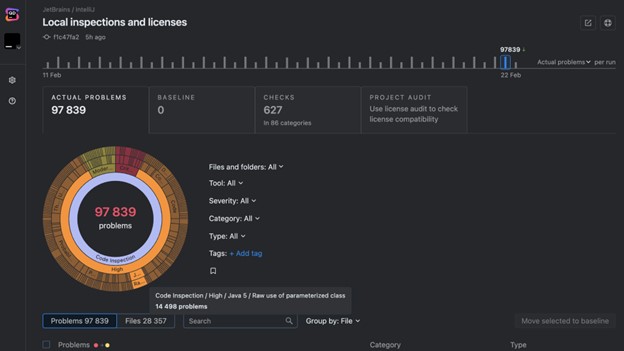
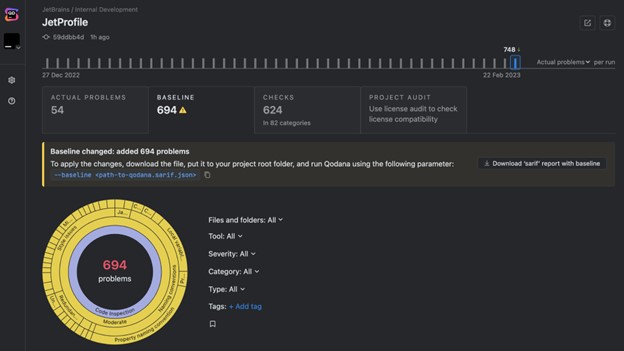
This is where advanced automation can have an outsize impact. By using automated and AI-guided testing, dev and QA teams can find and fix over 80% of conformance issues—without needing special accessibility knowledge!
The efficiency gains are immediate. Your teams can find more issues more quickly and address them earlier, saving both time and money, freeing them up to focus on more complex concerns, and consistently delivering the highest quality products.
Human-centric AI and automation in digital accessibility
As valuable and effective as AI and automated testing can be, human insight and expertise are still required. Automation doesn’t remove humans from the work; it enables humans to do their best work. And rather than replacing accessibility expertise, AI amplifies and scales it.
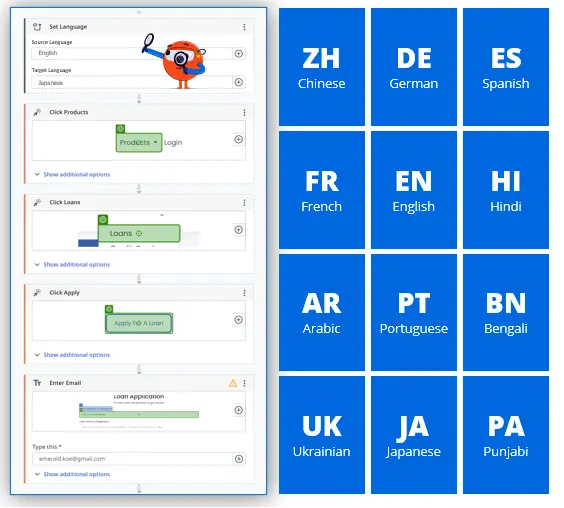
By leveraging what AI makes possible, we can empower dev and QA teams to accelerate velocity while maintaining quality. Recent updates from Deque, for example, introduce AI-driven capabilities that address the toughest accessibility challenges—increasing test coverage, reducing manual work, and making accessibility testing faster and easier than ever.
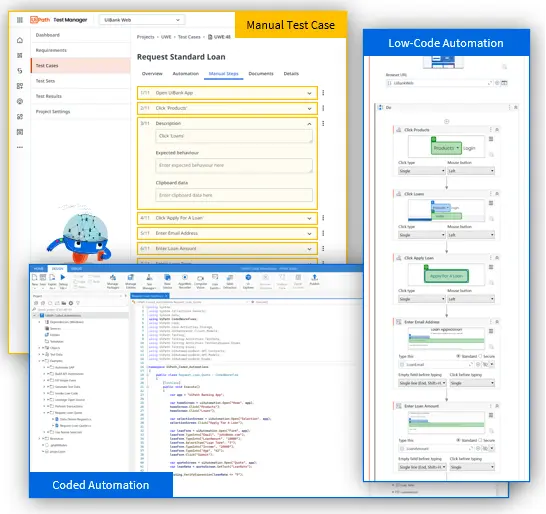
Saving time with tools for every part of the software development lifecycle
A comprehensive suite of accessibility testing tools that brings together automated testing and AI-guided testing can help your development and QA teams shift left and identify and fix accessibility issues early, with the highest levels of efficiency, and without the high false positive rates that hamper other solutions.
False positives—testing results that inaccurately flag issues that aren’t actually issues—waste your team’s time, and it’s why Deque is committed to zero false positives—because efficiency and accuracy matter.
It’s why our customers choose Deque and why developers and QA professionals prefer our tools. Because we help businesses become and stay accessible in the fastest and most cost-effective ways possible while delivering high-quality products and services for everyone. When it comes to digital accessibility, the proactive approach is the right approach.
Want to learn more? If you’re at EuroSTAR 2025, come see us about a free demo at Stand 34! You can also visit our website to request a free trial.
Author

Derrin Evers
Derrin Evers is a Senior Solution Consultant at Deque Europe. Derrin’s background and experience spans from design to development, small agencies to large enterprises, and public sector to private business from North America to Europe. With the professional goal to promote positive change within software development through digital accessibility, Derrin helps Deque customers discover, plan, and realize their potential through strategic and technical support across the software development lifecycle.
Deque were exhibitors In EuroSTAR 2025. Join us at EuroSTAR Conference in Oslo 15-18 June 2026.