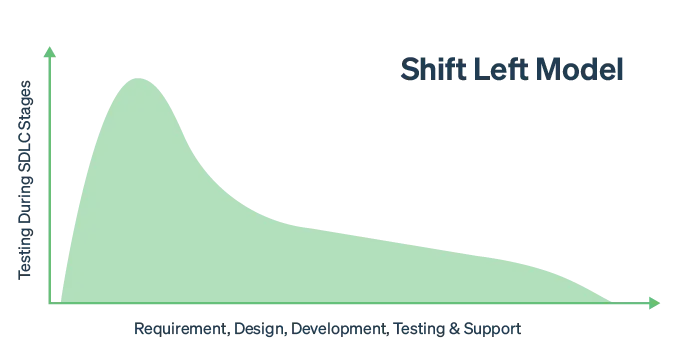
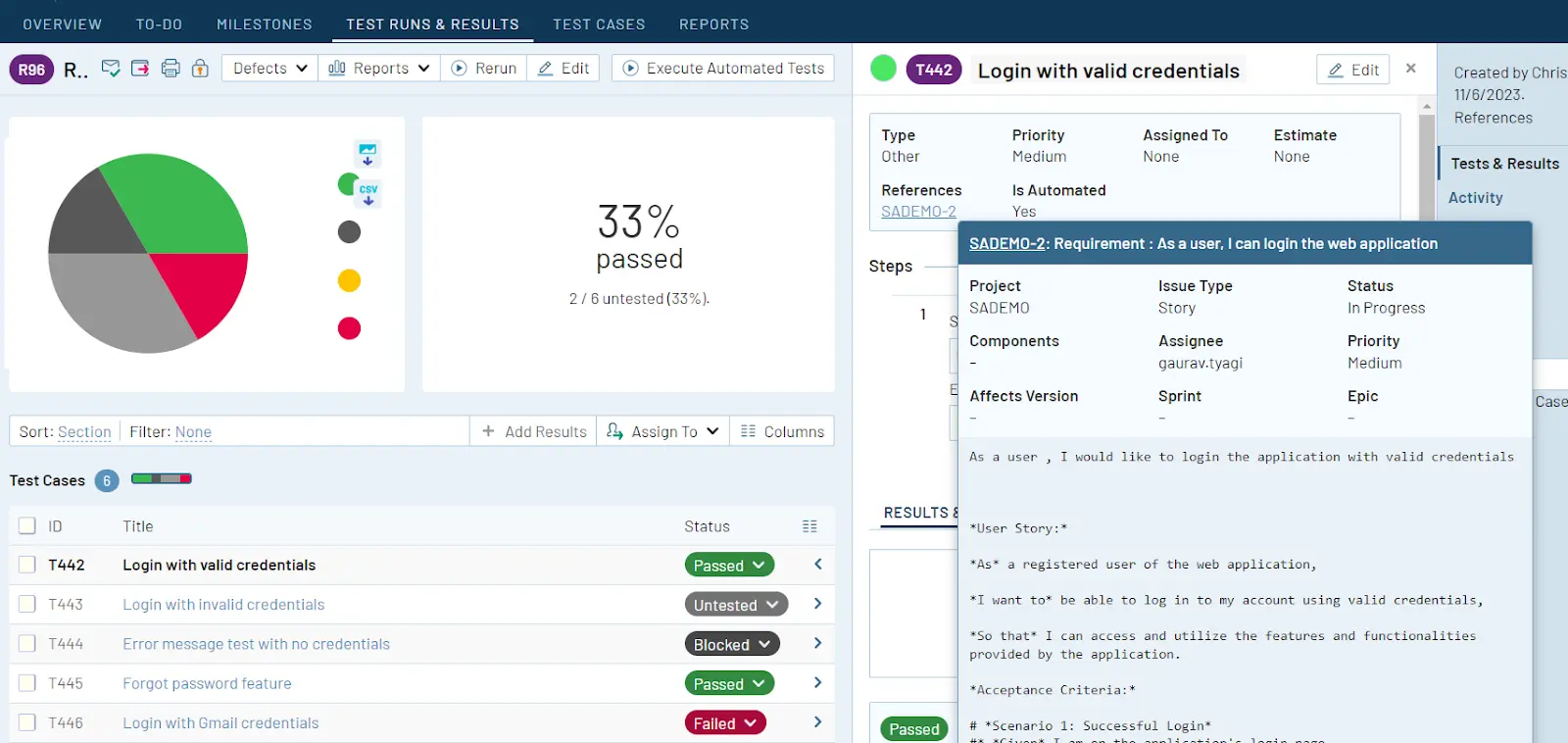
Test management is an integral part of software development that ensures that your software meets quality standards, is bug-free, and performs as expected. Unfortunately, there are some challenges in test management systems, causing significant issues while impacting application speed and quality. As software complexity grows, so do the difficulties in managing testing processes efficiently. To deal with the evolving challenges related to test management and software complexity, artificial intelligence (AI) plays a vital role. AI offers innovative solutions to many of these challenges. In this blog post, we’ll explore seven common test management challenges and how AI can solve them.
Navigating Key Challenges in Test Management
Efficient test management, improved productivity, increased ROI, and faster time to market are the things that every organization expects from its test management solutions. There are many aspects that stop companies from achieving the best results from their test management processes. They may experience inadequate test coverage, resulting from a lack of thorough testing across all possible scenarios, compromising the product’s quality and introducing the risk of undetected defects.
Similarly, inefficient test case prioritization leads to a misallocation of resources, with critical areas receiving insufficient attention. Thereby prolonging testing cycles and delaying time for the market. Moreover, insufficiently realistic test data fails to accurately simulate real-world scenarios, hindering the effectiveness of testing efforts and resulting in potential oversights. In case of having flaky test cases in test cycles, testers may experience inconsistency and uncertainty in the testing process. It can delay product release and affect ROI. These challenges collectively contribute to inefficient productivity, as valuable time and resources are wasted on ineffective testing methods. Efficiency suffers as testing cycles become prolonged and repetitive due to the need for rework and debugging. Consequently, ROI is impacted negatively as the cost of rectifying defects increases. Plus, the time to market is delayed, leading to missed opportunities and potential revenue loss. It is crucial to address these challenges effectively to optimize productivity, efficiency, ROI, and time to market in the software development lifecycle. Let’s learn how AI-powered solutions can address test management challenges.
1. Difficulty in Test Case Prioritization
In simple words, test case prioritization (TCP) refers to arranging test cases based on their significance, functionality, and potential impacts on the software and running them in the correct order. However, prioritizing test cases effectively is a challenging task in test management. With limited time and resources, it’s essential to focus your testing efforts on the most critical areas of an application.
Test Case Prioritization can help in efficient test management
Integration of AI in your test management solutions can help you with efficient test case prioritization. It analyzes factors like code changes, historical defect data, and business impact to automatically prioritize test cases. Machine learning algorithms can adapt over time, continuously improving prioritization based on past results and changing project requirements. By leveraging AI for test case prioritization, teams can optimize testing efforts and identify high-risk areas early in the development cycle.
It helps to Improve efficiency and reduce time to market as resources are allocated more effectively, ensuring that high-risk areas are thoroughly tested early in the development cycle.
2. Incomplete Test Coverage
Achieving comprehensive test coverage is essential for identifying potential defects and ensuring the overall quality of the software. In a traditional test management system, when test creation is a manual aspect, you may not have complete test coverage, leaving critical areas untested. This incomplete test coverage is a common challenge in software testing, leaving potential defects undetected. Besides manual issues, many other factors can lead to incomplete test coverage, such as time constraints, resource limitations, or oversight in test case creation. Incomplete test coverage increases the risk of releasing software with undiscovered bugs, which can lead to customer dissatisfaction, costly rework, and damage to the organization’s reputation.
Comprehensive test coverage can make test management better and improve productivity
To address the issue of incomplete test coverage, organizations can leverage artificial intelligence (AI) solutions that offer innovative approaches to test case generation, prioritization, and optimization. AI-powered test management tools can analyze application requirements and usage patterns to generate test cases automatically, ensuring comprehensive coverage across various scenarios and edge cases. By using AI for test case generation, teams can enhance the effectiveness of their testing efforts and minimize the risk of overlooking critical functionalities.
3. Availability of effective Test Data
Realistic and diverse test data plays a crucial role in effective software testing. It allows testers to simulate real-world scenarios and ensure comprehensive coverage of the application under test. However, generating and managing test data manually can be time-consuming and error prone. Plus, manually generated data may not always represent the diversity of data encountered in production environments. This can lead to insufficient test coverage and potentially overlook critical edge cases and scenarios.
Availability of effective Test Data improves productivity and reduces time to market
AI offers innovative solutions to address the challenge of test data availability by automating test data generation, management, and optimization. AI-driven test data generation tools can analyze application requirements and usage patterns to generate synthetic test data automatically. These tools use machine learning algorithms to simulate real-world scenarios, enabling thorough testing without compromising data privacy or security. Apart from synthetic test data generation, AI- AI tools can analyze existing data sources to profile and identify patterns, correlations, and anomalies within the data. Plus, AI-driven test data solutions can easily be integrated with existing testing workflows and tools, allowing testers to easily access and utilize generated test data within their testing environments. As a result, testers can conduct thorough testing without delays caused by manual data generation, improving productivity and time to market.
4. Bottlenecks Caused by Flaky Test Cases
A flaky test case is one that exhibits non-deterministic behavior when executed repeatedly within the same environment, resulting in intermittent results. Flaky test cases can cause delays and inconsistencies in test results and reduce the testing process’s reliability.
Flaky test case detection can help with efficiency and reduced time to market
AI-powered tools can analyze test scripts and execution logs to identify and address flakiness automatically. With machine learning algorithms, these testing tools can identify patterns indicative of flaky behavior and suggest corrective actions to ensure consistent and reliable test results. For instance, QMetry’s test management platform allows testers to gain control over flaky tests is identifying them using a “Flaky Score” derived from its execution history. With AI-powered flaky test detection and mitigation processes, testers can minimize disruptions in the testing process and improve the overall reliability of their testing efforts.
Flaky test detection not only increases efficiency and reduces time to market but also allows testers to focus on productive tasks without being hindered by inconsistent test results.
5. Unidentified Defects passing on final product
Detecting and resolving defects early in the development process is critical for delivering high-quality software. However, identifying potential defects among thousands of lines of code can be challenging, even for experienced testers.
Efficient defect detection helps with better test management, faster time to market, and improves ROI
AI-driven defect detection models can analyze code changes and historical defect data to identify patterns indicative of potential defects. Machine learning algorithms can predict which code changes are most likely to introduce defects, allowing developers and testers to focus their efforts on high-risk areas. By incorporating an AI-powered defect prediction system into their test management processes, testers can proactively address quality issues and minimize the impact of defects on the final product.
Therefore, AI-powered defect detection can help with better test management, faster time to market, and improved ROI as defects are detected and resolved before they impact the final product.
6. Managing Test Environment
Managing test environments with diverse configurations, dependencies, and constraints is a huge challenge for many development testing teams. When testers try to deploy and configure test environments manually, it can lead to inconsistencies, delays, and resource contention.
Better test environment management can Increase productivity and reduce time to market
AI-driven test environment management solutions can help testers to manage test environments in a better way. Using infrastructure as code (IaC) and configuration management tools, AI-powered solutions can automate test environment provisioning, configuration, and maintenance. Using machine learning algorithms, AI-driven solutions can optimize resource utilization, predict capacity requirements, and proactively identify potential bottlenecks or failures. By incorporating AI-driven test environment management into workflows, testers can ensure reliable and consistent test environments throughout the software development lifecycle. It influences increased productivity and reduced time to market as testers can focus on testing activities rather than dealing with manual deployment and configuration of test environments.
7. Test Result Analysis:
Test results analysis to identify trends or patterns plays a significant role in improving test coverage and reliability. In case of traditional test management systems, manually reviewing test results and logs is time-consuming and error-prone, especially in large-scale testing environments.
Efficient test result analysis can improve the efficiency and reliability of testing efforts
With AI integration, test result analysis becomes easy and more efficient. AI-powered test result analysis tools can aggregate and analyze test results from multiple sources, such as automated tests, manual tests, and performance tests. The application of machine learning algorithms enables these tools to identify correlations between test outcomes, code changes, and environmental factors. These tools can also perform root cause analysis and trend prediction. AI-driven test management tools allow testers to gain valuable insights into their testing processes and make data-driven decisions to improve quality and efficiency.
Key Takeaway
Test management can be complex and challenging with traditional methods and tools. However, AI offers innovative solutions to many of its inherent difficulties. AI-powered test management solutions offer technologies like machine learning, predictive analytics, and natural language processing to overcome common test management challenges and improve the efficiency, effectiveness, and reliability of their testing processes.
From test case prioritization to test environment management, AI-driven solutions have the potential to revolutionize the way software is tested and validated. AI can lead to faster release cycles, higher-quality products, and improved customer satisfaction. As AI continues to advance, its role in test management will only become more significant, empowering organizations to meet the demands of their users and sustain in a competitive software landscape.
Modern AI-powered tools like QMetry Test Management for Jira by QMetry can help you to manage all your testing activities through integrated tracking tools (e.g. Jira) and automation frameworks.
QMetry’s second-offering QMetry Test Management is designed for Agile and DevOps teams. These products are fully integrated into CI/CD pipelines giving testing teams and leaders full control over testing projects. These tools also manage manual testing seamlessly.
Both QMetry Test Management and QMetry Test Management for Jira offer scalable, compliant, and secured test management that allows you to deal with different testing challenges. Gen AI offerings of these tools have features like smart search, auto test case generation, and flaky test case detection making your testing super-efficient. These tools have potential of reducing time to market, improving ROI, and increasing efficiency.
Want to learn more about these test management products and how they can improve your test management experience? Schedule a call now!
Author

Deepak Parmar, Global Product Marketing Leader at Qmetry
QMetry is an innovative leader in AI enabled test management and automation products for Agile and DevOps teams that empower enterprises to build, manage, and deploy quality software at speed with confidence. QMetry is revolutionizing testing through AI-driven test authoring, test execution, and quality analytics for agile teams globally. Experience QMetry’s AI – enabled Test Management powered by QMetry Intelligence (Gen AI) delivering quality at speed and scale. It is a powerful, scalable, compliance driven quality orchestration platform that enables quality at speed with improved ROI.”
QMetry is an exhibitor at EuroSTAR 2024, join us in Stockholm.